Contrast Enhanced Mammography
What is Contrast Enhanced Mammography (CEM)?
Contrast-enhanced mammography is a quick breast imaging technique which combines 3D Tomosynthesis digital mammography with an intravenous contrast agent.
Contrast-Enhanced Mammography shows new or unusual blood flow patterns that develop when cancers grow. These highlighted areas make it easier to identify any cancer earlier.
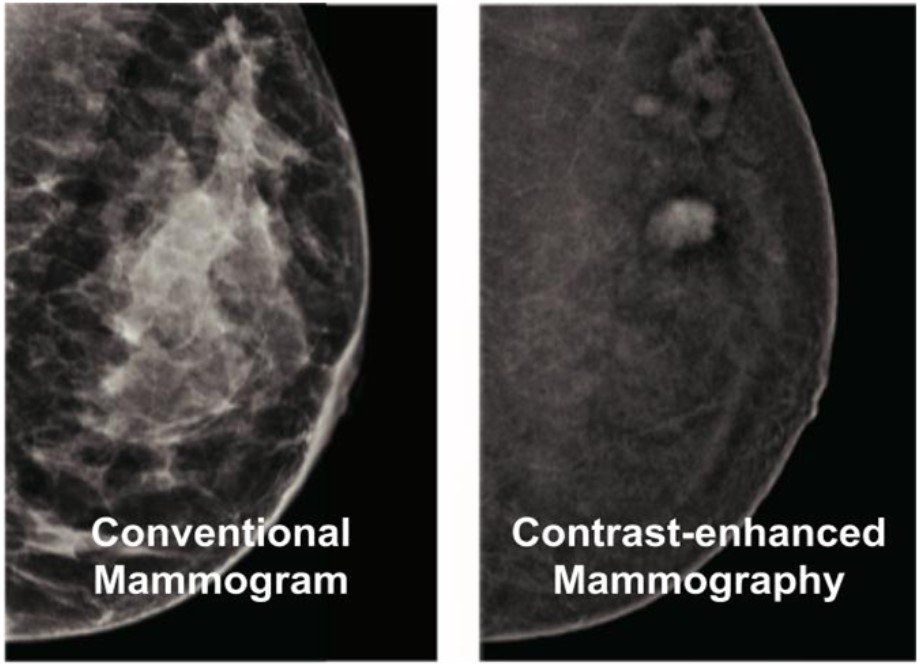
Contrast-Enhanced Mammography vs Normal Mammography
Mammograms are difficult to interpret, especially of cancers at their early stages.
A Contrast-Enhanced Mammogram examination provides additional information beyond a conventional mammogram.
It has been shown that a Contrast-Enhanced Mammogram can detect cancers that may not be visible on a standard mammogram, and offers improved reporting confidence.
Why a CEM Is Required?
Your doctor may recommend that you have a Contrast-Enhanced Mammogram exam for:
- Breast Cancer Screening for women with increased risk factors for Breast Cancer or women who have dense breasts
- Further evaluation of any breast lumps found during a physical exam
- Pre-Surgery Planning
- Post Treatment Surveillance
Benefits of Contrast-Enhanced Mammography
Early detection is the best defence against breast cancer and dramatically affect survival rates. Contrast-Enhanced Mammography:
- Increases the breast cancer detection rate,
- Provides better information about the extent of newly diagnosed breast cancers,
- Allows effective evaluation for breast cancer treatment planning
Contrast-Enhanced Mammography can save time and minimize anxiety as the test has the potential to reduce unnecessary breast imaging to a single investigation.
This reduces the need for additional tests such as:
Contrast-Enhanced Mammography also reduces the incidence of over-diagnosis of breast lesions and consequently minimises patient anxiety and the need for unnecessary biopsies.
Contrast-Enhanced Mammography offers other benefits including that it is:
- Unaffected by dense breast tissue,
- Lower cost and shorter procedure time compared to MRI, and
- Offers an effective alternative to breast MRI where MRI cannot be tolerated
How Does Contrast Enhanced Mammography Work?
Growing tumours need a blood supply, but the blood vessels created by the tumour are abnormal. When contrast is circulated via the blood these abnormal blood vessels leak contrast which accumulates in the tumour in sufficient concentration to allow X-ray imaging of its distribution.
Preparation for a Contrast Enhanced Mammography
CEM is a special type of mammogram that is performed after an IV injection of X-ray contrast (iodine-based).
Before you attend a Contrast-Enhanced Mammography appointment, a full medical history should be taken. Specifically including any prior conditions such as kidney (renal) function, diabetes, high blood pressure or any reactions to previous contrast.
If you are over 60 years of age, please ensure you have completed a recent blood test for renal function (within 3 months) called eGFR. This test checks your kidney function and creatinine levels.
On the Day of Your Contrast-Enhanced Mammography Procedure
Before You Attend
As with any contrast test in Radiology, we recommend you drink plenty of water before and after the test.
The contrast may cause some mild nausea, so only a light meal (such as soup) is recommended on the day of your exam.
Please avoid the use of deodorant, lotion, cream, powder, talc, oils, or perfume on the day of your CEM exam.
CEM Duration
A CEM exam takes about 15 minutes longer than a regular mammogram. This extra time is needed for the contrast portion of the test.
Because of the extra time to put in the IV line, the whole attendance at this appointment will be a little longer than a standard mammogram.
Intravenous Contrast
Your nurse or radiologist will insert an intravenous line in your arm (via a cannula) to administer the IV contrast dye containing iodine (the same dye as used in CT scans). You may feel a warm sensation as the IV contrast is inserted. This is normal.
Let your nurse or technologist know if you have pain at your IV site or if you feel any unusual symptoms such as itchiness, swelling, dizziness, difficulty breathing, or feeling like you are going to faint.
Two to three minutes after you receive the contrast, you will have your CEM exam.
CEM Examination
Two sequential images are taken at high and low energies. These two images are digitally subtracted to produce a single image that highlights abnormal vascularity, similar to the images produced by an MRI.
After Your CEM Exam
If you are going home after your CEM exam, the nurse will remove your IV and place a band-aid over the area.
Drink six to eight (8 ounces) glasses of water in the 24 hours after your CEDM exam. Drinking water will help remove the contrast from your body.
You can remove the band-aid after an hour if there is no bleeding.
What Are the Risks of CEM?
People who undergo CEM exams are exposed to slightly more radiation than people who have regular mammograms. This additional radiation is about the same as having one extra mammogram picture taken (e.g. five pictures instead of four).
Rarely, people can have an allergic reaction to intravenous (IV) contrast. Most reactions are mild, such as hives.
Some people can have more serious reactions, such as having trouble breathing or facial swelling. You should advise your doctor if you have had:
- Allergic reactions to iodinated contrast in the past,
- Kidney disease or poor kidney function,
- Diabetes and are on medication such as metformin, or
- Aged older than 60 years of age
a blood test to check the kidney function may be necessary.
Other Considerations Before Considering CEM
CEM is not advised for women who are pregnant. After childbirth, while breastfeeding, a CEM may be performed if necessary after discussion with your doctor.
CEM Results
Similar to a regular mammogram you may need additional tests to evaluate your CEM exam findings. These may include an ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a biopsy.
Download CEM Brochure